Random Access Memory (RAM) is a crucial component in computers, responsible for storing data that is actively being used or processed. It’s like the short-term memory of your computer, enabling quick access to information, which significantly affects the system’s overall speed and performance. Let’s delve into the various types of RAM, their features, form factors, and some common terms often associated with RAM, including a look at Video RAM (VRAM) used in graphics processing. 
- Types of RAM
- DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
- SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
- SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM)
- DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic RAM)
- VRAM (Video RAM)
- Form Factor Standards
- Common Terms Related to RAM
- Capacity
- – Example: 16GB RAM capacity is often recommended for gaming PCs to handle modern games efficiently.
- Speed
- Latency
- Bandwidth
- ECC (Error-Correcting Code)
- Dual-Channel and Quad-Channel
- VRAM in Detail
- Conclusion
Types of RAM
-
DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
DRAM is the most common type of RAM found in computers. It stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit. However, these capacitors tend to lose charge over time, requiring frequent refreshing to maintain data integrity.
– Features:
– High density and relatively low cost. – Requires constant refreshing, leading to higher power consumption. – Slower compared to SRAM due to refresh cycles. – Example: The memory modules used in most desktop and laptop computers, such as the 8GB DDR4 DRAM module found in a mid-range laptop.
-
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
Unlike DRAM, SRAM uses bistable latching circuitry to store each bit. This eliminates the need for periodic refreshing, making SRAM faster and more reliable.
– Features:
– Faster and more reliable than DRAM. – Does not need to be refreshed. – Higher cost and lower density compared to DRAM. – Typically used in cache memory and other applications requiring speed. – Example: L3 cache in a high-end Intel Core i7 processor.
-
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM)
SDRAM synchronizes with the system bus clock, ensuring that it operates in sync with the processor. This synchrony improves performance and efficiency.
– Features:
– Operates in sync with the CPU clock. – Higher speed and better performance than traditional DRAM. – Commonly used in modern computers. – Example: 4GB SDRAM module in an older desktop computer.
-
DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic RAM)
DDR SDRAM is an advanced version of SDRAM, capable of transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This effectively doubles the data transfer rate.
– Features:
– Doubles the data transfer rate compared to SDRAM. – Various generations, including DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5, each improving speed, bandwidth, and power efficiency. – Widely used in desktops, laptops, and servers. – Example: A 16GB DDR4 module in a gaming PC or workstation.
-
VRAM (Video RAM)
VRAM is a type of RAM specifically designed to store image data for display on a computer screen. It is used by graphics processing units (GPUs) to provide high-speed data access for rendering images and videos.
– Features:
– Optimized for high bandwidth and fast data access to handle complex graphics. – Often found in dedicated graphics cards. – Multiple types, including SGRAM, GDDR (Graphics DDR), and HBM (High Bandwidth Memory). – Example: An 8GB GDDR6 module in an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 graphics card.
Form Factor Standards
RAM modules come in different form factors, each designed to fit specific types of devices. The two most common form factors are DIMMs and SO-DIMMs.
-
DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module)
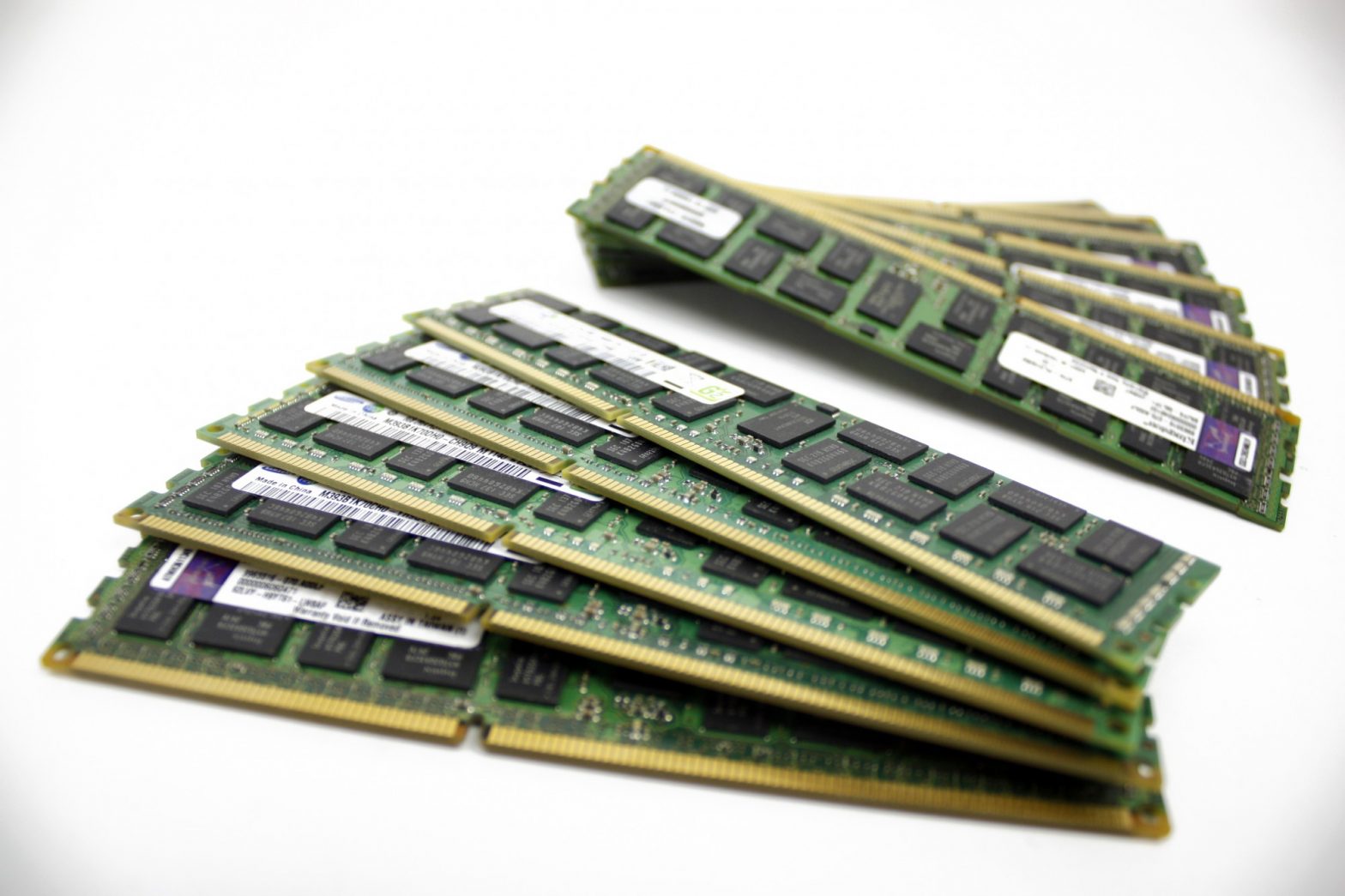 DIMMs are the standard form factor for desktop computers and servers. They have a larger size, allowing for more memory chips and, consequently, higher capacity.
DIMMs are the standard form factor for desktop computers and servers. They have a larger size, allowing for more memory chips and, consequently, higher capacity.
– Features:
– Larger physical size. – Higher capacity and speed. – Typically used in desktops and servers. – Example: A 32GB DDR4 DIMM module in a server or high-end desktop.
-
SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM)
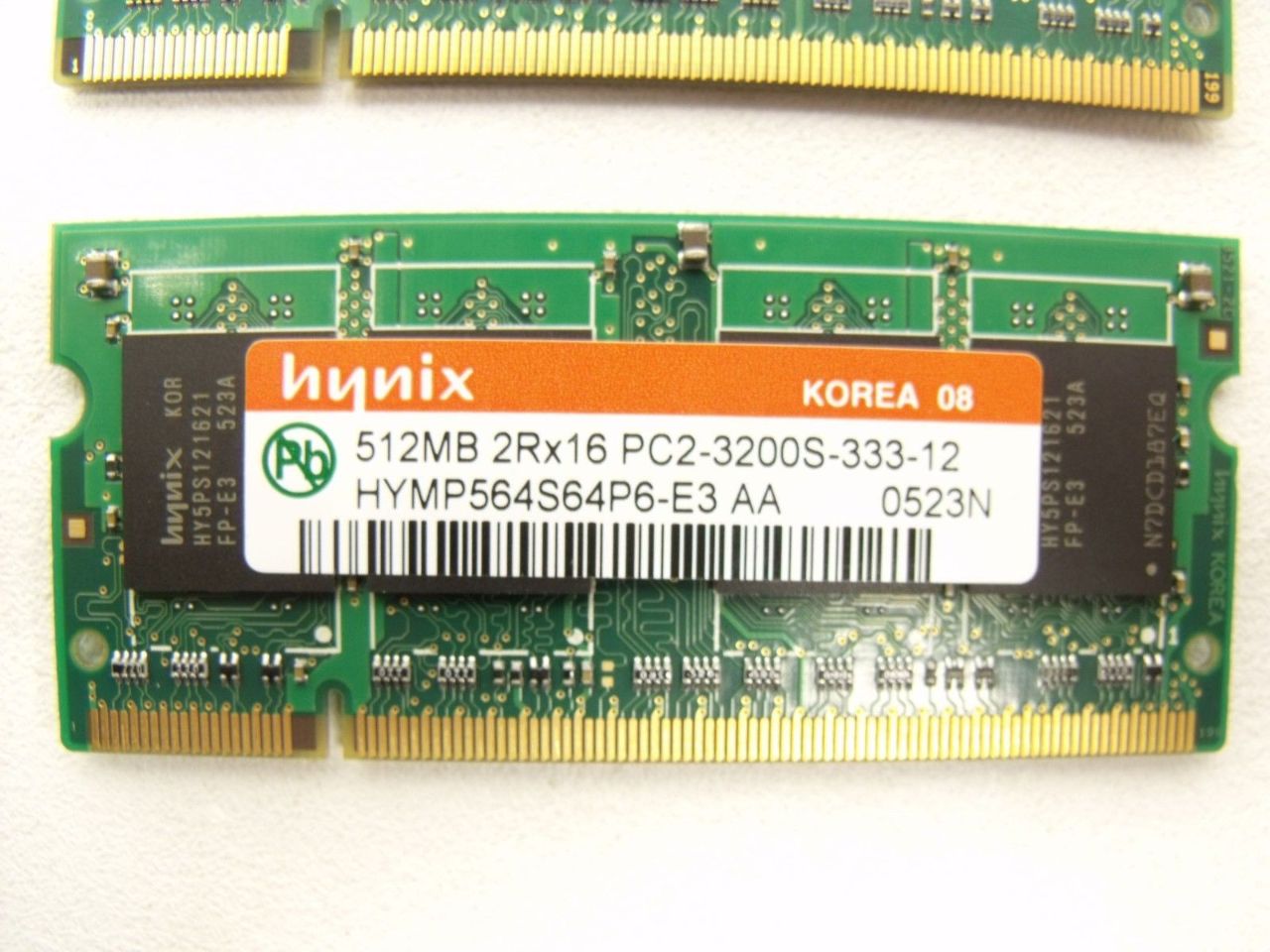 SO-DIMMs are a smaller variant of DIMMs, designed for laptops and compact devices where space is a premium.
SO-DIMMs are a smaller variant of DIMMs, designed for laptops and compact devices where space is a premium.
– Features:
– Smaller physical size. – Lower capacity compared to DIMMs but more than sufficient for laptops. – Commonly used in laptops and compact devices. – Example: An 8GB DDR4 SO-DIMM in a MacBook Pro.
Common Terms Related to RAM
When discussing RAM, several terms frequently come up. Understanding these terms can help in making informed decisions about RAM upgrades and performance expectations.
-
Capacity
Capacity refers to the amount of data RAM can store, measured in gigabytes (GB). Higher capacity allows for more applications to run simultaneously without slowing down the system.
– Example: 16GB RAM capacity is often recommended for gaming PCs to handle modern games efficiently.
-
Speed
RAM speed, measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz), indicates how quickly data can be read from or written to the RAM. Higher speeds mean better performance, especially in data-intensive applications.
– Example: A DDR4 RAM module with a speed of 3200MHz is considered fast and suitable for gaming and multimedia editing.
-
Latency
Latency, often measured in clock cycles, refers to the delay between a request for data and the actual delivery of the data. Lower latency is preferable as it means faster access to data.
– Example: CAS Latency 16 (CL16) on a DDR4 module indicates a lower latency, making it more responsive.
-
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the rate at which data can be transferred to and from the RAM. Higher bandwidth indicates a greater ability to handle large amounts of data quickly, which is crucial for tasks like gaming and video editing.
– Example: A DDR4 module with a bandwidth of 25.6GB/s can handle extensive data transfer requirements.
-
ECC (Error-Correcting Code)
ECC RAM includes additional error-detecting and correcting capabilities, ensuring data integrity by detecting and correcting common types of data corruption.
– Features:
– Used in servers and critical applications where data integrity is paramount. – Slightly slower and more expensive than non-ECC RAM due to the additional circuitry. – Example: 16GB ECC DDR4 RAM in a server environment to ensure data integrity.
-
Dual-Channel and Quad-Channel
Dual-channel and quad-channel refer to the use of multiple RAM sticks in parallel to increase data throughput. Dual-channel uses two sticks, while quad-channel uses four, improving performance by allowing simultaneous data transfers.
– Example: A dual-channel configuration using two 8GB DDR4 sticks in a gaming PC for improved performance.
VRAM in Detail
VRAM, or Video RAM, deserves a closer look as it plays a critical role in graphics performance. 
Types of VRAM
-
SGRAM (Synchronous Graphics RAM):
– A type of VRAM that synchronizes with the GPU clock, improving performance for graphics-intensive tasks.
-
GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate):
– GDDR variants (e.g., GDDR5, GDDR6) are commonly used in modern graphics cards. They provide high bandwidth and are optimized for rendering complex graphics. – Example: GDDR6 is used in NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX 30 series, delivering high performance for gaming and professional graphics work.
-
HBM (High Bandwidth Memory):
– HBM and HBM2 are newer types of VRAM that offer extremely high bandwidth and are used in high-end graphics cards. – Example: HBM2 is used in AMD’s Radeon Vega series, providing exceptional performance for demanding applications like 3D rendering and video editing.
Importance of VRAM
VRAM is crucial for tasks that require high-resolution textures and complex graphical computations. More VRAM allows for higher resolution textures, more detailed models, and smoother frame rates in games and professional applications. – Example: An 8GB GDDR6 VRAM in a graphics card can handle 4K gaming and virtual reality applications more effectively than a card with only 4GB, though 12GB is the minimum recommended for the current A title games.
Conclusion
RAM is a fundamental component in any computing device, significantly affecting performance and usability. Understanding the different types of RAM, such as DRAM, SRAM, and DDR variants, along with their features, helps in making informed choices for upgrades or new builds. Additionally, recognizing the importance of form factors like DIMMs and SO-DIMMs, and familiarizing oneself with common RAM-related terms, ensures a well-rounded grasp of how RAM contributes to overall system efficiency and performance. Furthermore, VRAM plays a critical role in graphics processing, making it essential for gaming and professional graphic work. Whether you’re a casual user or a tech enthusiast, knowing the intricacies of RAM and VRAM can enhance your computing experience and optimize your device’s performance.
We hope this article was helpful to you. You can follow us on X (Formerly Twitter), Instagram, LinkedIn and our WhatsApp Channel to keep updated with us and the latest tech.
Keep visiting GizmoGeek Hub, we are always happy to assist you and make your tech experience better!
Request – We are a new site and are solely dependent on the Ad revenue so we request you to not use any Ad blockers as it’s the only source of our income right now.